Arrays a kind of data structure that can store a fixed-size sequential collection of elements of the same type.
An array in C is a fixed-size collection of similar data items stored in contiguous memory locations. It can be used to store the collection of primitive data types such as int, char, float, etc., and also derived and user-defined data types such as pointers, structures, etc.

Declaring Arrays
In C, we have to declare the array like any other variable before using it. We can declare an array by specifying its name, the type of its elements, and the size of its dimensions. When we declare an array in C, the compiler allocates the memory block of the specified size to the array name.
Syntax :
data_type array_name [size]; // Single dimensional array
or
data_type array_name [size1] [size2]...[sizeN]; // Multi dimensional array
Array Initialization :
Initialization in C is the process to assign some initial value to the variable. When the array is declared or allocated memory, the elements of the array contain some garbage value. So, we need to initialize the array to some meaningful value. There are multiple ways in which we can initialize an array in C.
1. Array Initialization with Declaration with size :
In this method, we initialize the array along with its declaration. We use an initializer list to initialize multiple elements of the array. An initializer list is the list of values enclosed within braces { } separated b a comma.
data_type array_name [size] = {value1, value2, ... valueN};
2. Array Initialization with Declaration without Size :
If we initialize an array using an initializer list, we can skip declaring the size of the array as the compiler can automatically deduce the size of the array in these cases. The size of the array in these cases is equal to the number of elements present in the initializer list as the compiler can automatically deduce the size of the array.
The size of the arrays is 5 which is automatically deduced by the compiler.
data_type array_name[] = {1,2,3,4,5};3. Array Initialization after Declaration (Using Loops) :
We initialize the array after the declaration by assigning the initial value to each element individually. We can use for loop, while loop, or do-while loop to assign the value to each element of the array.
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
array_name[i] = valuei;
}Example of Array Initialization in C
// C Program to demonstrate array initialization
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
// array initialization using initialier list
int arr[5] = { 10, 20, 30, 40, 50 };
// array initialization using initializer list without
// specifying size
int arr1[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
// array initialization using for loop
float arr2[5];
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
arr2[i] = (float)i * 2.1;
}
return 0;
}Access Array Elements
We can access any element of an array in C using the array subscript operator [ ] and the index value i of the element.
array_name [index];One thing to note is that the indexing in the array always starts with 0, i.e., the first element is at index 0 and the last element is at N – 1 where N is the number of elements in the array.

Example of Accessing Array Elements using Array Subscript Operator
// C Program to illustrate element access using array
// subscript
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
// array declaration and initialization
int arr[5] = { 15, 25, 35, 45, 55 };
// accessing element at index 2 i.e 3rd element
printf("Element at arr[2]: %d\n", arr[2]);
// accessing element at index 4 i.e last element
printf("Element at arr[4]: %d\n", arr[4]);
// accessing element at index 0 i.e first element
printf("Element at arr[0]: %d", arr[0]);
return 0;
}
/*
Element at arr[2]: 35
Element at arr[4]: 55
Element at arr[0]: 15
*/Simple program to use of array :
// C Program to demonstrate the use of array
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
// array declaration and initialization
int arr[5] = { 10, 20, 30, 40, 50 };
// modifying element at index 2
arr[2] = 100;
// traversing array using for loop
printf("Elements in Array: ");
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
}
return 0;
}
/*
Elements in Array: 10 20 100 40 50
*/Update Array Element :
We can update the value of an element at the given index in a similar way to accessing an element by using the array subscript operator [ ] and assignment operator =.
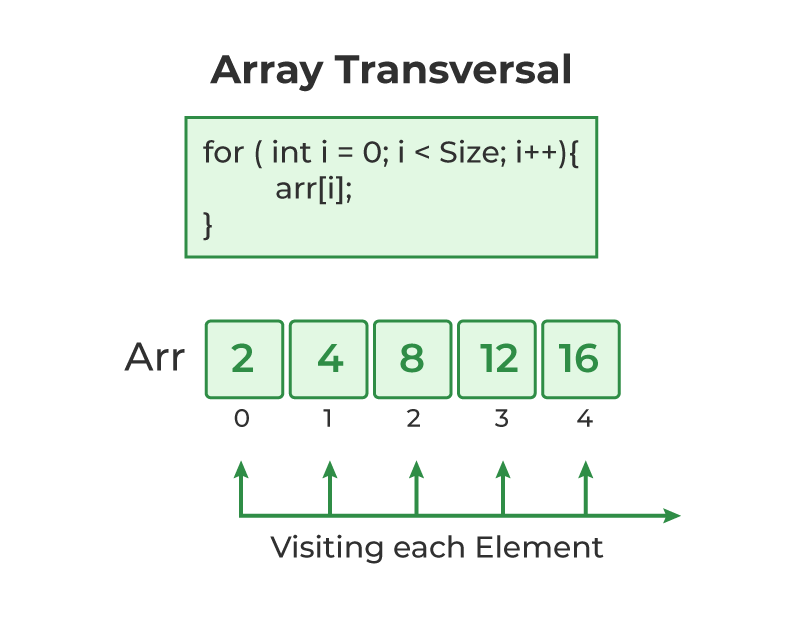
array_name[i] = new_value;C Array Traversal :
Traversal is the process in which we visit every element of the data structure. For C array traversal, we use loops to iterate through each element of the array.
Array Traversal using for Loop :
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
array_name[i];
}
Types of Array in C
There are two types of arrays based on the number of dimensions it has. They are as follows:
- One Dimensional Arrays (1-D Array)
- Multidimensional Arrays (2-D, 3-D)
One Dimensional Array in C
It is also known as 1-D arrays in C. The One-dimensional arrays are those arrays that have only one dimension.
Syntax :
array_name [size];
Array of characters(String)
In C, we store the words, i.e., a sequence of characters in the form of an array of characters terminated by a NULL character.
// C Program to illustrate strings
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
// creating array of character
char arr[6] = { 'G', 'e', 'e', 'k', 's', '\0' };
// printing string
int i = 0;
while (arr[i]) {
printf("%c", arr[i++]);
}
return 0;
}
/*
Output :
Geeks
*/Multidimensional Array in C
Multi-dimensional Arrays in C are those arrays that have more than one dimension. Some of the popular multidimensional arrays are 2D arrays and 3D arrays.
A. Two-Dimensional Array in C
A Two-Dimensional array or 2D array in C is an array that has exactly two dimensions. They can be visualized in the form of rows and columns organized in a two-dimensional plane.
Syntax of 2D Array in C:
array_name[size1] [size2];
Here,
size1: Size of the first dimension.
size2: Size of the second dimension.
Example of 2D Array
// C Program to illustrate 2d array
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
// declaring and initializing 2d array
int arr[2][3] = { 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60 };
printf("2D Array:\n");
// printing 2d array
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
printf("%d ",arr[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
/*
Output:
2D Array:
10 20 30
40 50 60
*/Three-Dimensional Array in C
Another popular form of a multi-dimensional array is Three Dimensional Array or 3D Array. A 3D array has exactly three dimensions. It can be visualized as a collection of 2D arrays stacked on top of each other to create the third dimension.
Syntax of 3D Array in C
array_name [size1] [size2] [size3];

Example :
// C Program to illustrate the 3d array
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
// 3D array declaration
int arr[2][2][2] = { 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60 };
// printing elements
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 2; j++) {
for (int k = 0; k < 2; k++) {
printf("%d ", arr[i][j][k]);
}
printf("\n");
}
printf("\n \n");
}
return 0;
}
/*
Output:
10 20
30 40
50 60
0 0
*/Arrays and Pointers :
Arrays and Pointers are closely related to each other such that we can use pointers to perform all the possible operations of the array. The array name is a constant pointer to the first element of the array and the array decays to the pointers when passed to the function.
// C Program to demonstrate the relation between arrays and
// pointers
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int arr[5] = { 10, 20, 30, 40, 50 };
int* ptr = &arr[0];
// comparing address of first element and address stored
// inside array name
printf("Address Stored in Array name: %p\nAddress of "
"1st Array Element: %p\n",
arr, &arr[0]);
// printing array elements using pointers
printf("Array elements using pointer: ");
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
printf("%d ", *ptr++);
}
return 0;
}
/*
Output :
Address Stored in Array name: 0x7ffce72c2660
Address of 1st Array Element: 0x7ffce72c2660
Array elements using pointer: 10 20 30 40 50
*/Passing an Array to a Function in C
An array is always passed as pointers to a function in C. Whenever we try to pass an array to a function, it decays to the pointer and then passed as a pointer to the first element of an array.
// C Program to pass an array to a function
#include <stdio.h>
void printArray(int arr[])
{
printf("Size of Array in Functions: %d\n", sizeof(arr));
printf("Array Elements: ");
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
printf("%d ",arr[i]);
}
}
// driver code
int main()
{
int arr[5] = { 10, 20, 30, 40, 50 };
printf("Size of Array in main(): %d\n", sizeof(arr));
printArray(arr);
return 0;
}
/*
Output :
Size of Array in main(): 20
Size of Array in Functions: 8
Array Elements: 10 20 30 40 50
*/Return an Array from a Function in C
// C Program to return array from a function
#include <stdio.h>
// function
int* func()
{
static int arr[5] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
return arr;
}
// driver code
int main()
{
int* ptr = func();
printf("Array Elements: ");
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
printf("%d ", *ptr++);
}
return 0;
}
/*
Output:
Array Elements: 1 2 3 4 5
*/- Fixed Size
The array in C is a fixed-size collection of elements. The size of the array must be known at the compile time and it cannot be changed once it is declared. - Homogeneous Collection
We can only store one type of element in an array. There is no restriction on the number of elements but the type of all of these elements must be the same. - Indexing in Array
The array index always starts with 0 in C language. It means that the index of the first element of the array will be 0 and the last element will be N – 1. - Dimensions of an Array
A dimension of an array is the number of indexes required to refer to an element in the array. It is the number of directions in which you can grow the array size. - Contiguous Storage
All the elements in the array are stored continuously one after another in the memory. It is one of the defining properties of the array in C which is also the reason why random access is possible in the array. - Random Access
The array in C provides random access to its element i.e we can get to a random element at any index of the array in constant time complexity just by using its index number.
Advantages of Array in C
The following are the main advantages of an array:
- Random and fast access of elements using the array index.
- Use of fewer lines of code as it creates a single array of multiple elements.
- Traversal through the array becomes easy using a single loop.
- Sorting becomes easy as it can be accomplished by writing fewer lines of code.
Disadvantages of Array in C
- Allows a fixed number of elements to be entered which is decided at the time of declaration. Unlike a linked list, an array in C is not dynamic.
- Insertion and deletion of elements can be costly since the elements are needed to be rearranged after insertion and deletion.
Programming example
C Program to perform array input and output.
// C Program to perform input and output on array
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
// declaring an integer array
int arr[5];
// taking input to array elements one by one
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
scanf("%d", &arr[i]);
}
// printing array elements
printf("Array Elements: ");
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
}
return 0;
}
/*
Input:
5 7 9 1 4
Output:
Array Elements: 5 7 9 1 4
*/C Program to print the average of the given list of numbers
// C Program to the average to two numbers
#include <stdio.h>
// function to calculate average of the function
float getAverage(float* arr, int size)
{
int sum = 0;
// calculating cumulative sum of all the array elements
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
sum += arr[i];
}
// returning average
return sum / size;
}
// driver code
int main()
{
// declaring and initializing array
float arr[5] = { 10, 20, 30, 40, 50 };
// size of array using sizeof operator
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(float);
// printing array elements
printf("Array Elements: ");
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
printf("%.0f ", arr[i]);
}
// calling getAverage function and printing average
printf("\nAverage: %.2f", getAverage(arr, n));
return 0;
}
/*
Output :
Array Elements: 10 20 30 40 50
Average: 30.00
*/C Program to find the largest number in the array.
// C Program to find the largest number in the array.
#include <stdio.h>
// function to return max value
int getMax(int* arr, int size)
{
int max = arr[0];
for (int i = 1; i < size; i++) {
if (max < arr[i]) {
max = arr[i];
}
}
return max;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int arr[10]
= { 135, 165, 1, 16, 511, 65, 654, 654, 169, 4 };
printf("Largest Number in the Array: %d",
getMax(arr, 10));
return 0;
}
/*
Output :
Largest Number in the Array: 654
*/What is the difference between Arrays and Pointers?
| Pointer | Array |
|---|---|
| A pointer is a derived data type that can store the address of other variables. | An array is a homogeneous collection of items of any type such as int, char, etc. |
| Pointers are allocated at run time. | Arrays are allocated at runtime. |
| The pointer is a single variable. | An array is a collection of variables of the same type. |
| Dynamic in Nature | Static in Nature. |
